- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Lunatin-1: a membrane-disruptive peptide isolated from Hadruroides lunatus scorpion venom with cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line
Posted by
Luis A. Roque
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Lunatin-1: a membrane-disruptive peptide isolated from Hadruroides lunatus scorpion venom with cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line
Abstract
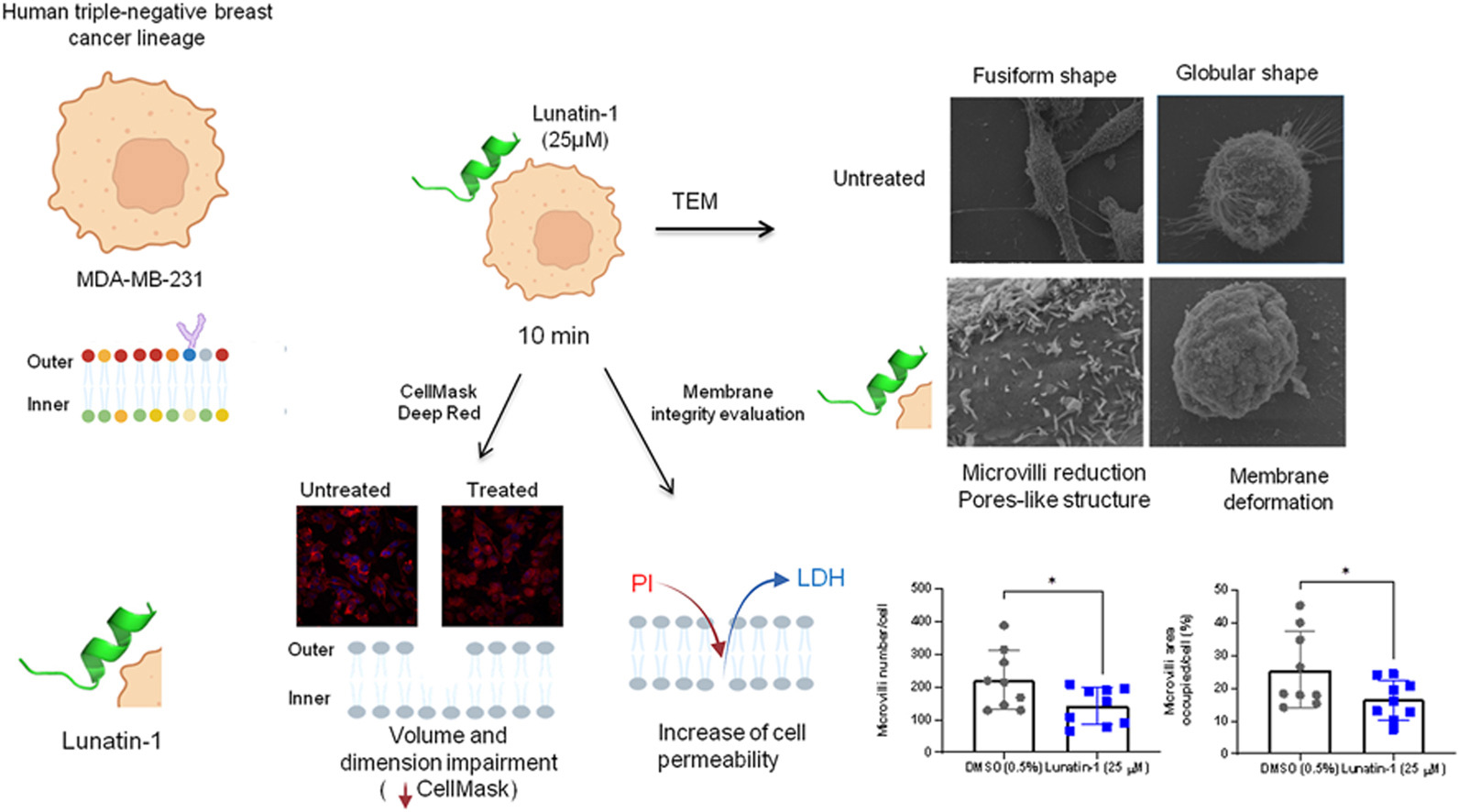
Membrane-disrupting peptides - including antimicrobial and antitumor peptides - disrupt cell membrane through pore formation. Strategies for using these peptides as adjuvants in cancer treatment regimens have been investigated. In the context of a high recurrence rate and ineffective postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy treatment in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), the potential antitumor cytotoxic effect of Lunatin-1 was evaluated for the first time in the TNBC cell line MDA-MB-231. Synthetic Lunatin-1 was purified and its purity confirmed by mass spectrometry. Cytotoxicity of this peptide against MDA-MB-231 cells was associated with a rapid increase in propidium iodide-positive cells and LDH release through the loss of membrane integrity in a concentration and time-dependent manner. Staining with CellMask Deep Red to outline the cell membrane showed its disruption 5 min after Lunatin-1 treatment, which was not associated with necroptosis. Ultrastructural analysis by scanning electron microscopy showed membrane damage due to microvilli reduction and increased density of pores per cell compared to untreated cells. We concluded that Lunatin-1 is a membrane-disruptive peptide in this cellular model, highlighting it as an interesting tool for conjugating with cancer markers or anticancer drugs.
De Sousa Gomes, K., Raíssa-Oliveira, B., Schildknecht, S., De Lima, M. E., Melo-Braga, M. N., Gomes, D. A., De Castro Pimenta, A. M., Verano-Braga, T., Leist, M., & De Souza-Fagundes, E. M. (2025). Lunatin-1: A membrane-disruptive peptide isolated from Hadruroides lunatus scorpion venom with cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. Biochimie. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2025.06.006
Citotoxicity
Hadruroides lunatus
Lunatin-1
MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell
Peptides
scorpion
Scorpiones
Toxinology
Venomics
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps